A turnaround is a crucial event in the lifecycle of a processing plant that involves shutting down, maintenance, and recommissioning of the facility. It is a complex process that requires the coordination of multiple activities and resources to ensure the plant returns to its normal operation. To ensure that the turnaround is successful, it is essential to plan and execute it efficiently, considering the various risks and uncertainties associated with the process.
One of the critical aspects of turnaround planning is determining the optimum scope for inclusion in the turnaround worklist. It involves identifying the work orders that are essential for the turnaround's success and eliminating the ones that are not. The optimum scope determination is crucial because it helps in saving the planner's manhours, building comprehensive estimates of personnel and materials, and avoiding the wasting of resources for work orders that are later descoped.
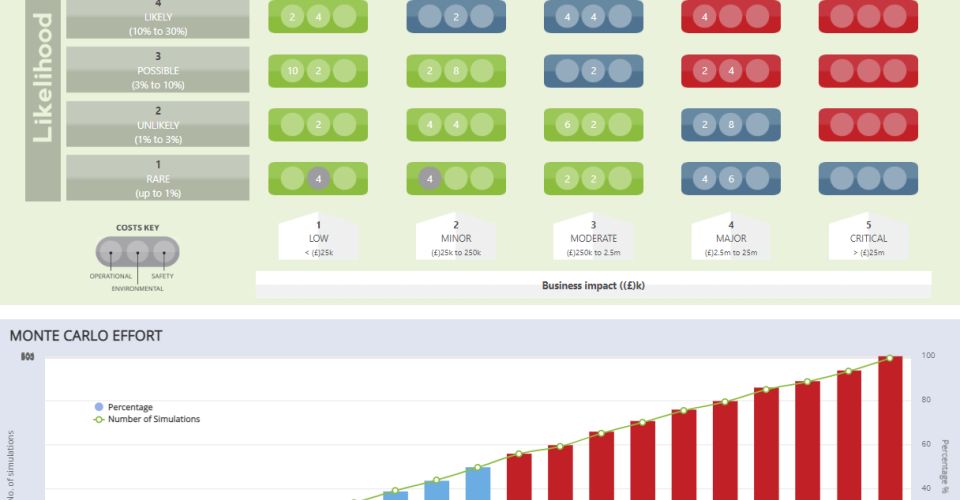
To determine the optimum scope for the turnaround worklist, Monte Carlo Risk-Based Simulation (MC-RBS) can be used effectively. MC-RBS is a statistical method that involves running multiple simulations to evaluate the impact of different risk factors on the outcome. The simulation provides a range of outcomes based on the probabilities of different risk factors, which can then be used to identify the most likely scenario and help Turnaround planners make informed decisions.
MC-RBS can be used in several ways to determine the optimum scope for the turnaround worklist. Firstly, it can be used to identify the critical work orders that are necessary for the turnaround's success. The simulation can evaluate the impact of different work orders on the turnaround schedule and identify the ones that are critical to the success of the process. By eliminating the non-critical work orders, the turnaround team can focus on the essential work and minimize the risk of delays and overspending.
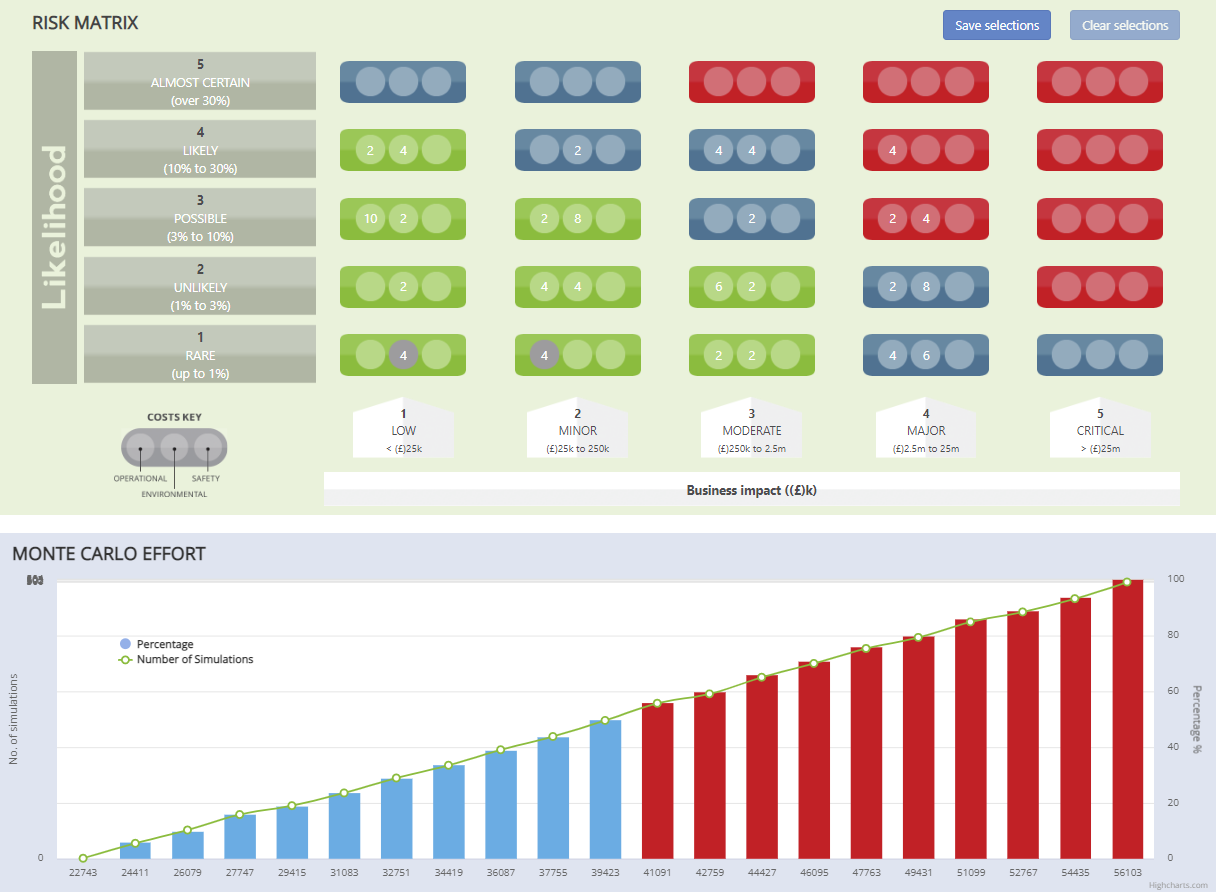
Another way that MC-RBS can be used to determine the optimum scope is by evaluating the impact of different risks on the turnaround schedule. In future release of iPlan, the simulation may also evaluate the impact of different risks such as weather conditions, supply chain disruptions, and unexpected maintenance issues on the turnaround schedule. Based on the results of the simulation, the turnaround team can prioritize the work orders that are most vulnerable to the risks and ensure that they are included in the worklist.
By using Monte Carlo Risk simulation in iPlan, the turnaround team can quickly estimate the resources for each potential Turnaround work order. The simulation results can then be used to build an accurate manhour requirement for the turnaround, which can help in avoiding overloading the plant owners budget, minimizing the risk of financial losses.
Finally, MC-RBS can be used to identify work orders not to be included in the Turnaround worklist (descoped). By running multiple simulations, the turnaround team can evaluate the impact of different risks and uncertainties on the work orders. Based on the results of the simulation, the team can identify the work orders that are most vulnerable to the risks and make informed decisions on whether to include them in the worklist or descope them.
In conclusion, Monte Carlo Risk-Based Simulation is an effective tool that can be used to determine the optimum scope for inclusion in a turnaround worklist. By using MC-RBS, the turnaround team can identify the critical work orders, evaluate the impact of different risks on the schedule, build estimates of personnel and materials quickly, and identify which work orders are descoped. By utilizing MC-RBS, the turnaround team can ensure that the process is executed efficiently, effectively, and with minimal risk, leading to the greater likelihood of a successful turnaround.